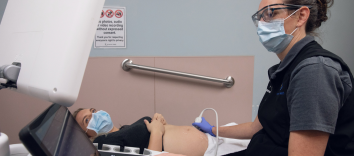
Ultrasound (also called sonography) uses high frequency sound waves to produce images of the body. A transducer is moved over the part of the body being imaged and sends and receives sound waves which are then interpreted to produce an image on a computer screen. The interpretation of the sound waves is based on the length of time for the echo to bounce back and the character of the sound (i.e. whether it is a solid, water, or gas).
Resources
Frequently Asked Questions
Are patients allowed to have companions during medical imaging exams?
Patient companions often provide patients with a sense of physical and/or emotional safety while the patient is having a medical imaging procedure performed. Learn more
Find Locations
STAY CONNECTED